This article will provide an in-depth comparison of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Spravato (esketamine) as treatments for depression, helping individuals understand their options and make informed decisions in consultation with their healthcare providers.
Today, depression is the most common mental health disorder around the world, and rates are rising. Moreover, there are different responses to existing treatments, many of which are limited. For that reason, it’s necessary to explore different treatment options for those who have limited responses or treatment-resistant depression. This article will focus on Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Spravato (esketamine).
What is TMS?
When looking at TMS vs Spravato, you first need to understand how TMS works. Transcranial magnetic stimulation is an outpatient form of treatment that can be used regularly to combat depression. This process works by placing electrodes or a similar device over the head from which magnetic pulses are sent into specific, targeted deep regions of the brain which cannot necessarily be reached by medication.
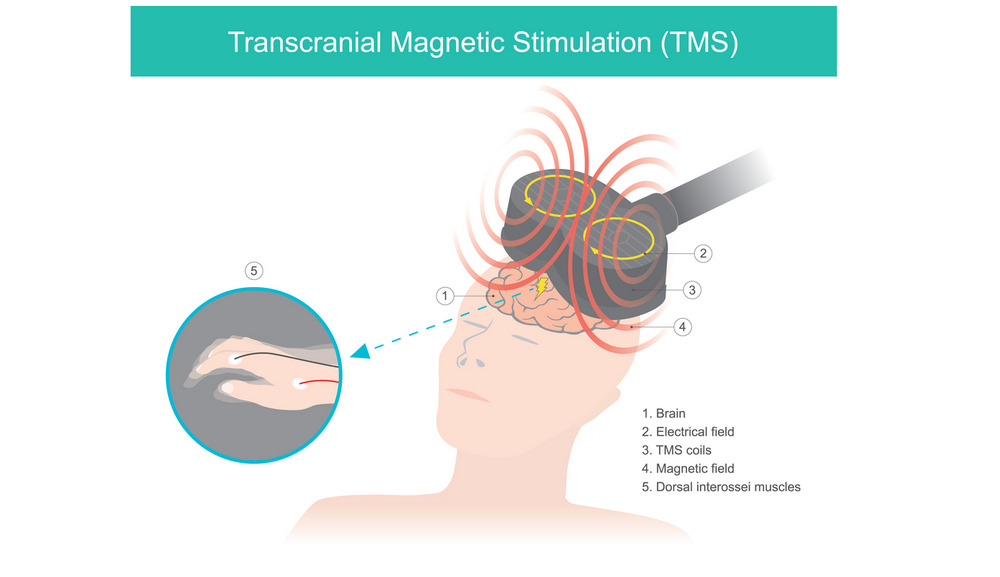
Transcranial magnetic stimulation is a non-invasive form of treatment that has become a very popular alternative to treat several conditions including depression. It is approved by the FDA and works by stimulating deeper regions of the brain in such a way that encourages them to perform the way they should. underperforming regions of the brain like the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex are often responsible for depression symptoms.
What is Spravato?
Spravato is a nasal spray that is a prescription version of ketamine. Spravato is the brand name for “esketamine.” Ketamine has been used as an anesthetic for surgical purposes since the 1970s.
Ketamine is a derivative of PCP, called angel dust. When used as an anesthetic, it provides quick relief for depression and anxiety symptoms, which prompted Yale researchers to investigate it in the 1990s as a form of depression treatment.
Over the next several decades, studies were published supporting the rapid improvement of symptoms in patients with treatment-resistant depression or major depressive disorder with suicidal ideations in particular.
Ketamine interacts with different subsets of neurotransmitters by improving communication and regrowing glutamate receptors on the ends of your nerve cells.
These glutamate receptors are responsible for sending and receiving messages in the brain, but depression symptoms can inhibit the efficacy of this communication, which reduces mood and brain function.
It was approved by the FDA specifically for major depressive disorder presenting with suicidal thoughts and treatment-resistant depression. It is only administered through restrictive programs offered by certified facilities as an outpatient treatment.
When you go to a clinic for Spravato, you’ll be seated comfortably, and a healthcare provider will explain how to use the nasal spray. They will tell you when to do it and how much to use and watch you administer it. They’ll give you a treatment schedule, and you’ll have to be under the supervision of a licensed clinic each time you use the nasal spray.
After you have used the nasal spray you will also have to remain under supervision for several hours to check for any potential side effects. In general patients receive six doses that are administered over the span of two or three weeks.
How Do TMS and Spravato Work?
When you are looking at how TMS and spravato work the biggest difference is their mechanism of action. TMS changes your neural activity, targeting areas in the dendrites and the axons.
Pharmacological medicine like Spravato changes regulatory mechanisms by directly targeting neural receptors in the brain.
Another key difference is that Spravato is distributed systematically and gets absorbed through the stomach and the bloodstream, which means you don’t get a concerted amount, and it remains in a ready state in your blood. TMS, by comparison, can have varying degrees of intensity that are strictly measured, targeting specific structures in your brain applied at different times based on the amount of neural activity that’s going on.
Let’s look at that in a bit more detail.
The Mechanism of Action of TMS
Transcranial magnetic stimulation works by sending magnetic pulses at different frequencies into targeted areas of the brain like the:
- medial prefrontal cortex,
- dorsolateral prefrontal cortex,
- inferior frontal gyrus,
- superior parietal lobe,
- middle temporal gyrus,
- superior temporal sulcus,
- lateral occipital cortex
- supplementary motor area/paracentral gyrus
This is done by placing a device over the head like a helmet or electrodes. From there a technician controls the exact location, depth, and frequency of the magnetic pulses.
These magnetic pulses are sent at varying speeds based on your needs into specific, predetermined areas of the brain. Transcranial magnetic stimulation usually starts with a few sessions dedicated toward brain mapping.
Brain mapping improves the efficacy of TMS as a treatment for depression by figuring out where specific regions of your brain are located. Everybody has a slightly different brain in terms of size and structure although the general locations remain the same. Brain mapping allows a technician to pinpoint the exact areas that need to be stimulated as part of your ongoing treatment.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation is an outpatient procedure. It is a non-surgical, non-invasive procedure that does not require any type of anesthesia or other medication. This means:
- You can drive yourself to and from your appointments.
- You will not have any recovery time or problems going back to your regular schedule.
The sessions themselves are relatively short, an average of 20 minutes. This short time frame means that you can easily fit five sessions throughout the week so that you can receive the full range of your treatment plan within a matter of weeks.
Physiological and neurological impacts of TMS
So, what are the physiological and neurological impacts of TMS? Your brain is an electrochemical organ, which means it relies on electricity. Neurons in your brain have to fire electrically to communicate with one another, and when they do that, they send ions into an electrical field that can actually be measured. Your brain concurrently responds to electrical fields outside of the body.
TMS creates an electrical field above the scalp and applies energy into your brain in order to modulate your neural activity in areas that are dysfunctional and causing symptoms of depression.
When looking at TMS or spravato, TMS works very differently by utilizing your brain’s natural plasticity to stimulate long-term changes.
The use of TMS encourages things like:
- Improved blood flow in blood vessels that are not performing the way they should
- Increased circulation to areas of the brain that are under or overperforming
- Better neural growth and improved communication between different sections of the brain.
The Mechanism of Action of Spravato
Esketamine (Spravato) works in the brain of someone with TRD or MDD by improving the shrinkage in the hippocampus, which affects people with depression by up to 20%. The hippocampus is associated with memory and learning.
Moreover, over time, depression can damage the glutamate receptors located on the ends of your nerve cells. This impedes overall communication in the brain.
Once taken, Spravato improves connections in the brain, like the hippocampus, that have been damaged by depression. It does so by improving the circuitry function and communication, regrowing areas of the brain that have subsequently been damaged, like the hippocampus and the glutamate receptors.
Physiological and neurological impacts of Spravato
Spravato helps to regrow glutamate receptors, which improves nerve cell function and communication and, in so doing, boosts mood and eliminates depression symptoms. This helps to regrow the synapses that have died as a result of major depressive disorder or treatment resistant depression.
Comparing Efficacy and Safety of TMS vs Spravato
For the last several decades, a lot of research has gone into the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation for treating mental health conditions.
- In 2008, TMS was approved by the FDA for depression.
- In 2019, Spravato was approved as a nasal spray for depression by the FDA, but only when used in conjunction with antidepressants.
Clinical trials and outcomes
Meta-analyses have found TMS to be an effective form of treatment for depression anxiety and a way to minimize issues like chronic pain, migraines, and substance abuse disorders. While most symptom changes only last for one year this offers a much more viable solution for long-term improvement compared to medication.
- An average of 1/3 of treatment-resistant depression cases achieve complete remission after using transcranial magnetic stimulation.
- An average of 3/4 of patients see significant improvements in their depression symptoms.
- Recent work has indicated that those who have developed a tolerance to antidepressants show significant improvement when using TMS.
- Research has found that those who have developed a tolerance to antidepressants can see improvement in as little as two weeks.
- Literature reviews have found that response rates for those with a major depressive disorder are high, between 50% and 55% with 30% of people receiving complete remission.
- Imaging research has found that stimulation of the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex and the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex improves the efficacy of TMS for depression.
- Functional connectivity studies indicate clinical improvements when TMS therapy is used for major depressive disorder or treatment-resistant depression.
- Hundreds of clinical TMS sites have confirmed that where antidepressants were ineffective, TMS worked for depression, with over 37% remission rates.
So what about Spravato?
- Between 35.6% and 46.1% of those with depression go into remission after using Spravato.
- 70% of those who use Spravato have at least a 50% reduction in depression symptoms.
- Studies indicate that 62% of patients see better social functioning while on spravato.
- 53% of patients report better quality of life using Spravato.
- 41% of patients report that they are better able to work after taking Spravato.
- 30% of patients are in a position to meet basic needs that were previously ignored.
- 34% of patients indicate a general improvement in their overall health with Spravato.
Note:
When you look at Spravato vs. TMS, one of the key things to be aware of is that the FDA has only approved the use of Spravato when used in conjunction with an antidepressant. So, for people who have treatment-resistant depression or who have developed a tolerance to antidepressants, they will still have to contend with the side effects of the antidepressant, even knowing that said half of the equation will not work for them.
Speed of onset of treatment benefits with spravato and TMS
One of the biggest benefits associated with transcranial magnetic stimulation is the speed of onset of treatment benefits. Many patients notice improvements right away, after just five sessions on average. This means that in less than one week, you can experience improvement in your depression.
With spravato, the length of time it takes for your treatment session is relatively short, effectively the amount of time it takes for you to use the nasal spray. However you still have to remain at the clinic for observation which means that sessions last significantly longer than what you would get with TMS.
However, the onset of improvement in symptoms happens rapidly. People can enjoy relief almost immediately. For this reason, it is highly effective for people who are struggling with suicidal ideations.
Safety and Side Effects
When you are looking at spravato and TMS, you also need to consider safety and side effects.
TMS safety and side effects
Transcranial magnetic stimulation is one of the safest forms of treatment you could choose for depression. Unlike medication of any kind, there are next to no side effects whatsoever associated with transcranial magnetic stimulation. At most, people experience things like tingling sensations, headaches, or slight discomfort in the area where the electrodes were placed.
However, this is an uncommon side effect, and among those who experience it, it tends to go away after the first few sessions.
The process is completely safe and does not cause severe pain. At most, people feel mild sensations related to the magnetic pulses but you have control over the intensity of those magnetic pulses as well.
Other than those who have an electrical component surgically installed in their brains or who suffer from epilepsy, there are no other disqualifying conditions that would mean you cannot use transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression. This means that it is something widely available to everyone, including those with pre-existing health conditions, those with concurrent conditions, and pregnant women.
Spravato safety and side effects
Because spravato is ketamine based, there is a potential side effect for abuse and ketamine addiction, which is one of the most critical side effects and safety concerns. However, to mitigate this risk, the FDA has only allowed this medication to be administered as part of a federal program that undergoes heavy monitoring.
Any clinic or treatment center that offers spravato must participate in the FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) program.
This means:
- The clinic has to be registered with the FDA.
- Patients must sign waivers and forms explaining that they understand the rules of this preventative measure and will abide by them.
- Patients must follow the nasal spray use as outlined by the clinic and are only allowed a set amount each visit as prescribed by the clinic.
- The clinic must adhere to certain safety precautions.
- As the patient, you have to remain at the clinic for up to 2 hours after each treatment so that any potential side effects can be monitored.
Other side effects include:
- Feeling intoxicated or high
- Lack of energy
- Headache
- Dissociation
- Sedation
- Drowsiness
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
- Nausea
You will need someone to drive you to and from each appointment because of these side effects.
There are several safety risks depending on your circumstances and pre-existing conditions, including:
- Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding
- Those with psychotic disorders
- Patients with a history of substance abuse
- Patients with liver problems
- Those with a history of stroke or heart attack
- Patients with heart or brain problems
- Those with hypertension
- Anyone taking medications like central nervous system depressants, psychostimulants, or monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Antidepressants/Antipsychotics
A caveat to those who want to use spravato is that the FDA requires it be used in conjunction with an antidepressant or an antipsychotic.
Antidepressants come with many side effects including:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Problems reaching orgasm
- Reduced sexual desire
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Loss of appetite
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Agitation
- Dizziness
- Restlessness
- Blurred vision
- Difficulty urinating
- Dry mouth
- Weight gain
Antipsychotics come with several side effects as well, including:
- Tremors
- Muscle stiffness
- Agitation
- Restlessness
- Dizziness, especially when transitioning from lying down to sitting up
- Rapid weight gain
Increased risk of diabetes - Sleepiness
- Low energy
- Dry mouth
- Fluid retention
- Blurred vision
- Loss of menstrual periods for women
Long-term health concerns or benefits
When you are looking at spravato vs. TMS, you also need to compare the long-term health concerns and benefits.
TMS longevity
With transcranial magnetic stimulation, you will generally be given a recommendation for the appropriate number of sessions to treat your depressive disorder. This can be anywhere between 20 sessions and 40 sessions. However, as mentioned, most people get relief within a matter of a few sessions, a figure that continues to increase with time.
Once that treatment regimen is completed, most patients enjoy long-term Health Improvement or remission. Among the people who get positive changes and remission, those changes last an average of one year. Transcranial magnetic stimulation does not permanently change the brain, as it does rely heavily on the neuroplasticity of the brain to be effective in the first place and this plasticity allows the brain to revert to older patterns that may have contributed to or caused depression.
To that end, those who are considering transcranial magnetic stimulation can be done with a treatment in a matter of weeks, after which they can enjoy a reduction in symptoms for an average of one year. But following that, they will likely need to continue an annual use of transcranial magnetic stimulation as part of regular treatment to manage depression symptoms.
Co-occurring conditions and TMS
Another benefit long-term to using TMS vs. spravato is that transcranial magnetic stimulation can be used to treat several co-occurring conditions at the same time whereas the medication cannot.
In particular, there are several conditions that often co-occur, such as depression and anxiety. These tend to come from the same deeper regions of the brain, so transcranial magnetic stimulation sessions that reach these areas might subsequently make improvements to co-occurring disorders like anxiety disorders.
That said, some studies indicate that spravato can also help reduce anxiety symptoms because of its ability to improve glutamate receptor growth and communication in areas of the brain that tend to overlap with regard to depression and anxiety symptoms.
Spravato longevity
Given that spravato received FDA approval in 2019, there hasn’t really been adequate time to study long-term efficacy. As of now the use of this nasal spray must be used with an antipsychotic or antidepressant medication and those medications can have long-term effects on metabolic changes, blood pressure, or weight gain.
Oral antidepressants also come with a wide range of negative side effects that pose potential long-term risks for users who choose spravato because, again, spravato is only administered in conjunction with an antidepressant or antipsychotic medication.
TMS and Spravato Together
TMS and Spravato can be used together. One of the nice things about transcranial magnetic stimulation is that there are no ill effects when combined with any other treatment. In fact, for many people, it is recommended that it not be the exclusive form of treatment but rather a part of an existing treatment plan.
If you are struggling with depression and you are trying to decide between spravato and TMS, you can use both at the same time or try one and then the other to determine the efficacy.
Summing Up
If you are struggling with depression, you might consider TMS and spravato as two potential treatments. Choosing the right treatment should be based on your individual needs as well as medical advice. The type of depression disorder you have will influence which method works best and whether or not you should consider TMS and spravato together. Don’t be afraid to consult with healthcare providers for a personalized treatment approach.